Search Results for survey
Explore AI generated designs, images, art and prompts by top community artists and designers.
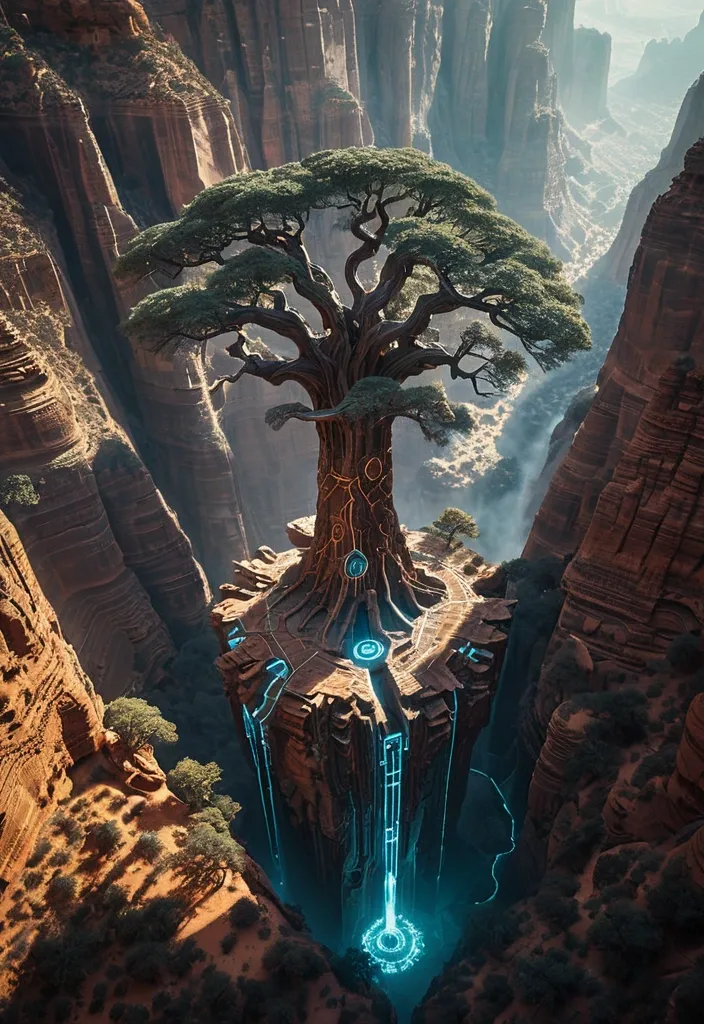

A colossal ancient tree with circuitry patterns embedded in its bark , its roots reaching into a vast , unexplored canyon system bathed in ethereal light. A single , small drone hovers near the canopy , surveying the scene. The image should evoke a sense of awe and mystery , blending natural grandeur with advanced , ancient technology. Shot with a wide-angle cinematic lens , capturing the immense scale and atmospheric depth , reminiscent of fantasy concept art. ,
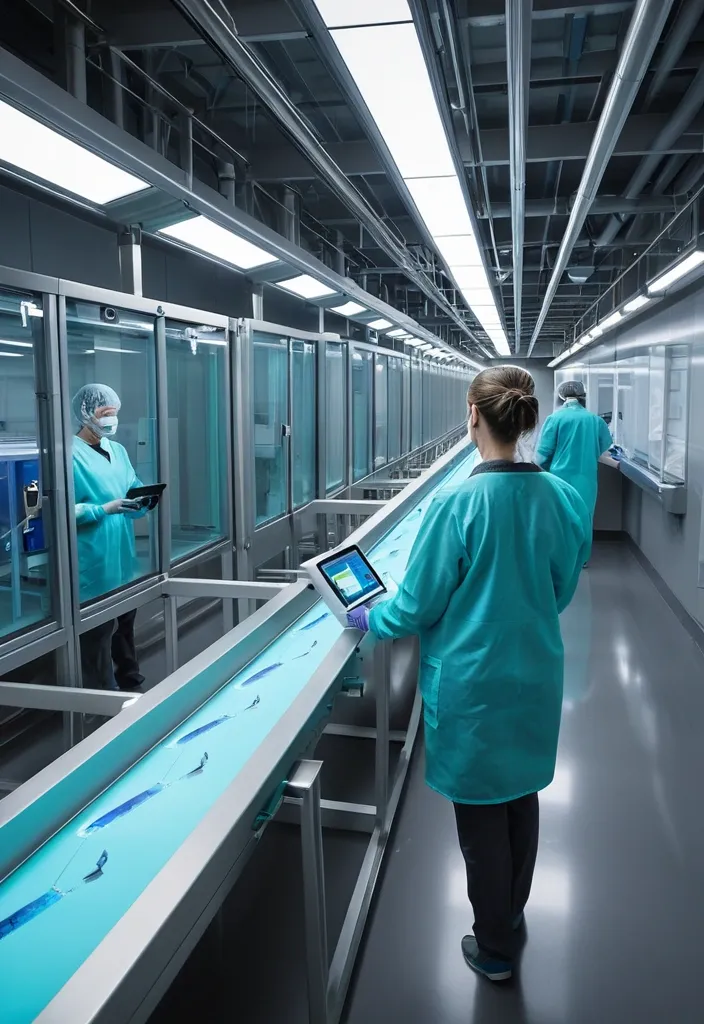

In a clinical veterinary corridor staffed by technicians wearing teal protective smocks and digital tablets , each ostrich pauses briefly within a transparent scanning arch that emits soft blue light as sensors capture heart rate , gait patterns , and temperature. A conveyor-like walkway gently moves the birds forward while robotic arms with padded ends perform non-contact feather sampling for DNA and disease checks. Stainless steel testing stations line the walls , with sample tubes , sealed containers , and diagnostic screens displaying real-time data under sharp industrial LED lighting. An overhead crane-mounted camera angle surveys the entire corridor , capturing the synchronized precision of staff and machines as the screening process flows without interruption. ultra-realistic , cinematic , professional , high-detail 4K , documentary style ,
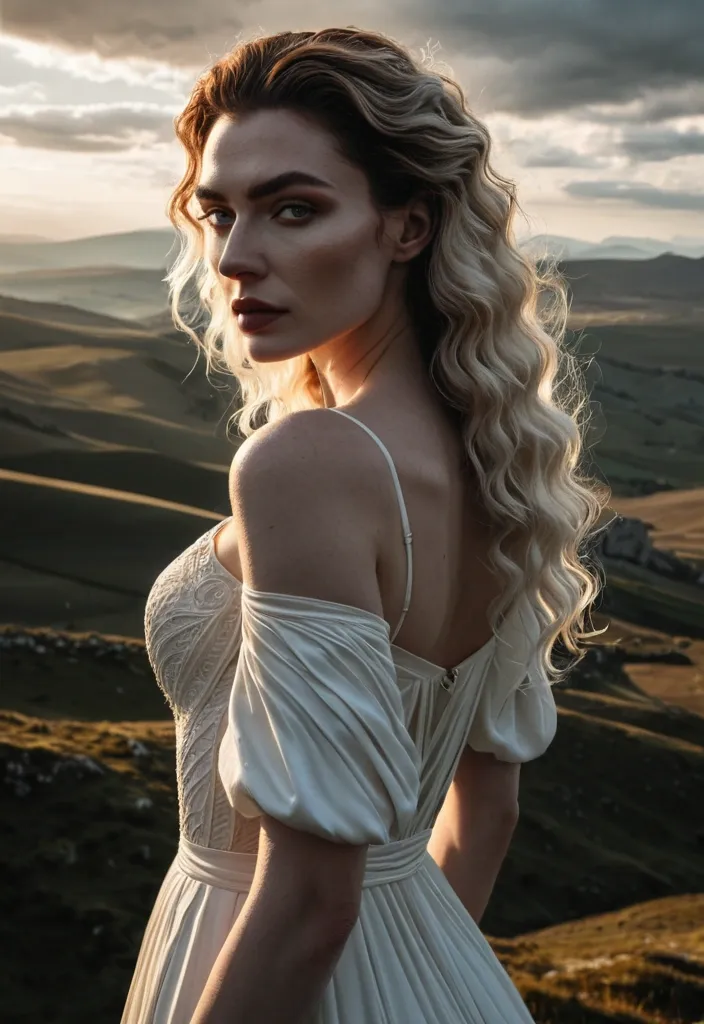

A beautiful European pale female with wavy shoulder brown hair in her mid thirty , wearing blue opened wide zipper open-side tactic suit , is standing fairly in a post apocalyptic street , she have a futuristic laser gun in right hand with survey equipment is posed next to her , crimson desert planet , gazing up at a swirling text "ai" is a sacred syllable , that dominates the night sky. In the distance , monolithic , geometric structures of an unknown alien civilization pierce the horizon. The scene evokes a sense of profound isolation and the immensity of cosmic history. Rendered in a hyper-realistic , cinematic style with an emphasis on vast landscapes and dramatic lighting. ,
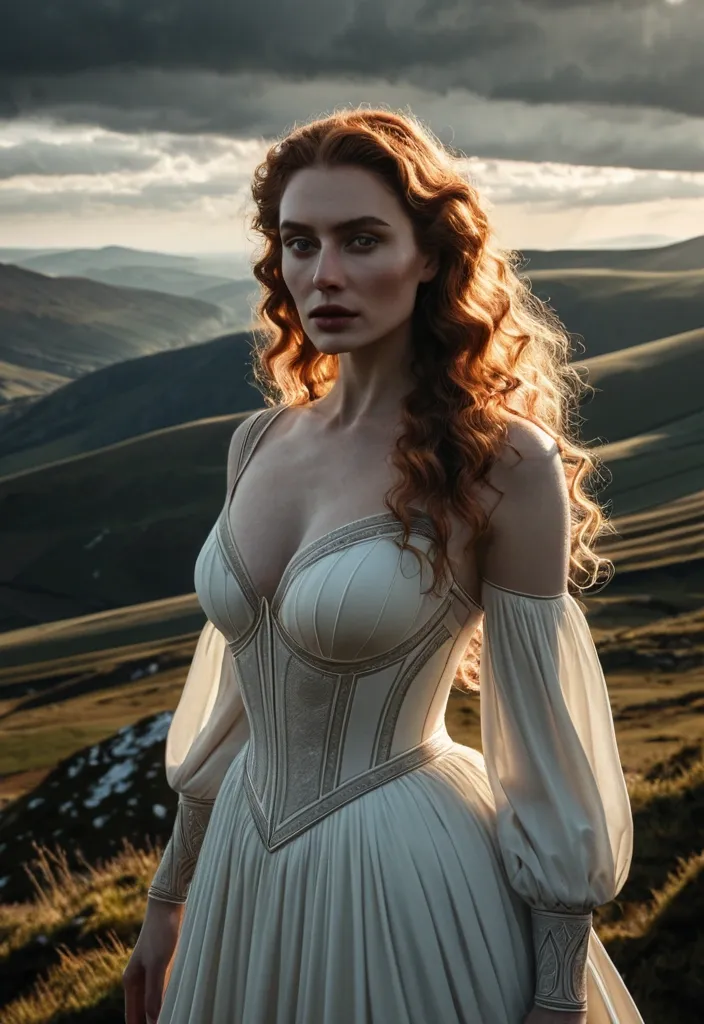

A beautiful European pale female with wavy shoulder brown hair in her mid thirty , wearing blue opened wide zipper open-side tactic suit , is standing fairly in a post apocalyptic street , she have a futuristic laser gun in right hand with survey equipment is posed next to her , crimson desert planet , gazing up at a swirling text "ai" is a sacred syllable , that dominates the night sky. In the distance , monolithic , geometric structures of an unknown alien civilization pierce the horizon. The scene evokes a sense of profound isolation and the immensity of cosmic history. Rendered in a hyper-realistic , cinematic style with an emphasis on vast landscapes and dramatic lighting. ,
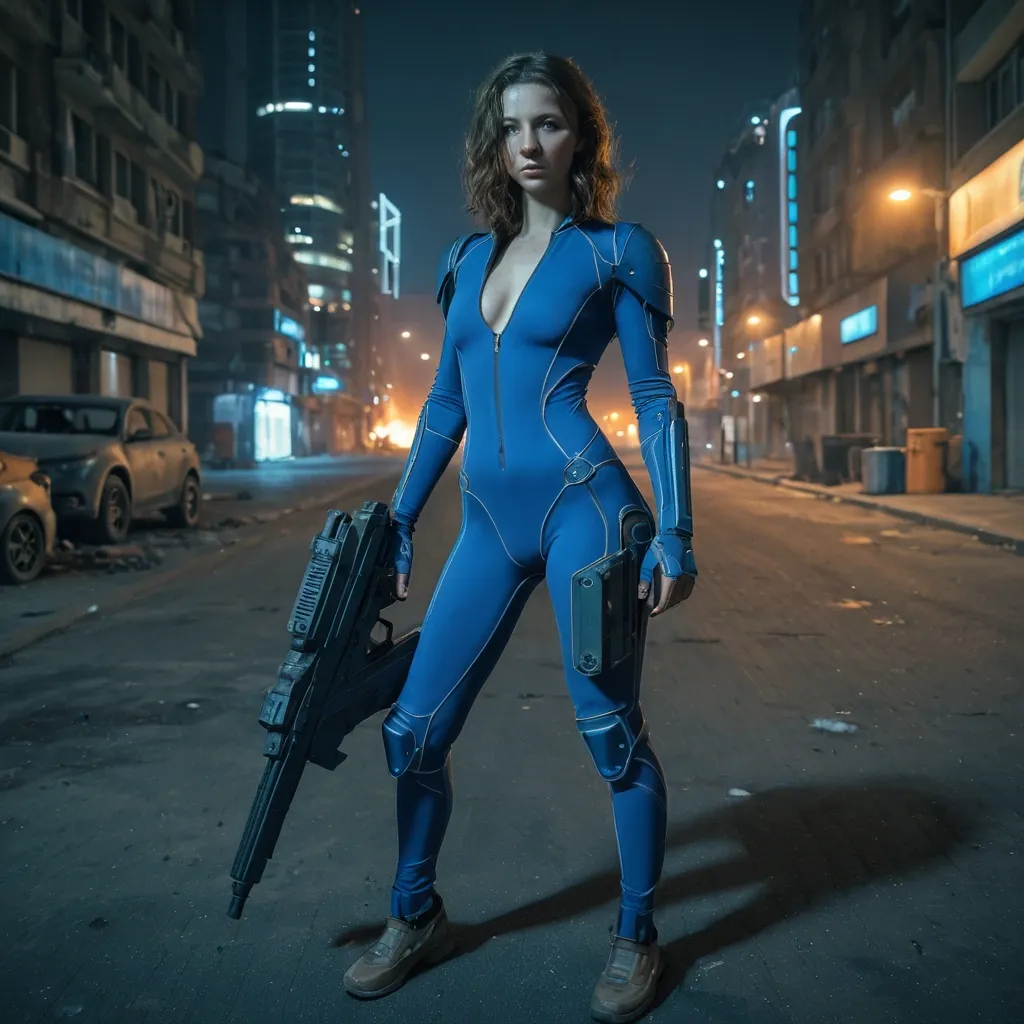

full lenght , a beautiful european pale female with wavy shoulder brown hair in her mid thirty , wearing blue opened wide zipper openside spandex suit , is standing fierly in a post apocalyptic street , she have a futuristic laser gun in right hand , backpack with survey equipment is posed next to her , a burning futuristic city in the background , it's night , cinematic style ,
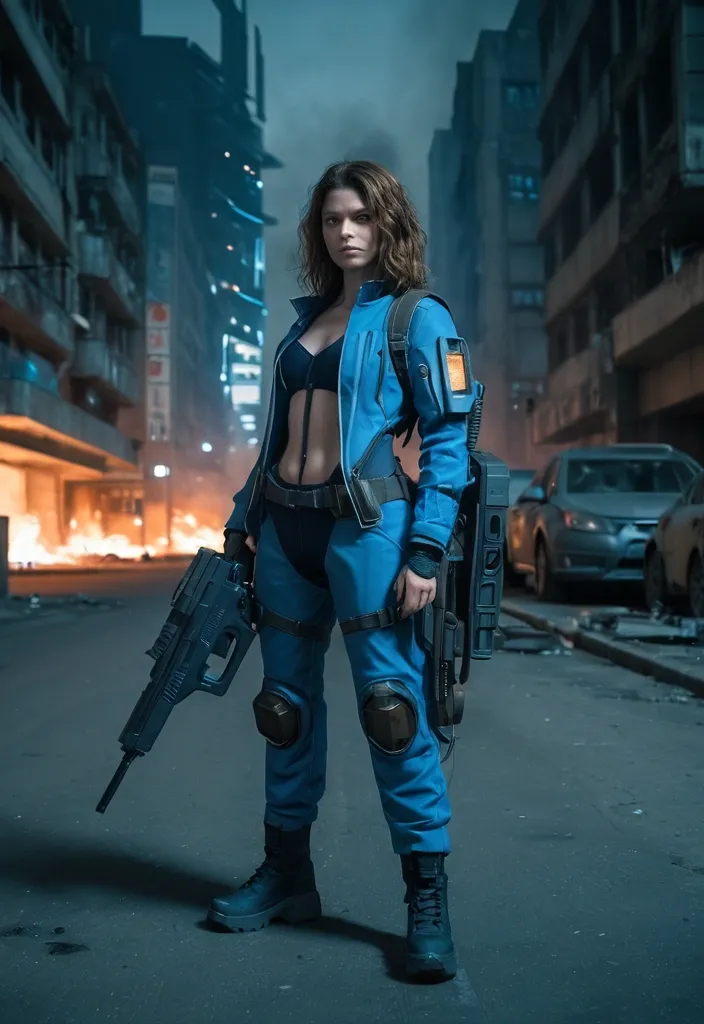

full lenght , a beautiful european pale female with wavy shoulder brown hair in her mid thirty , wearing blue opened wide zipper openside tactic suit , is standing fierly in a post apocalyptic street , she have a futuristic laser gun in right hand , backpack with survey equipment is posed next to her , a burning futuristic city in the background , it's night , cinematic style ,
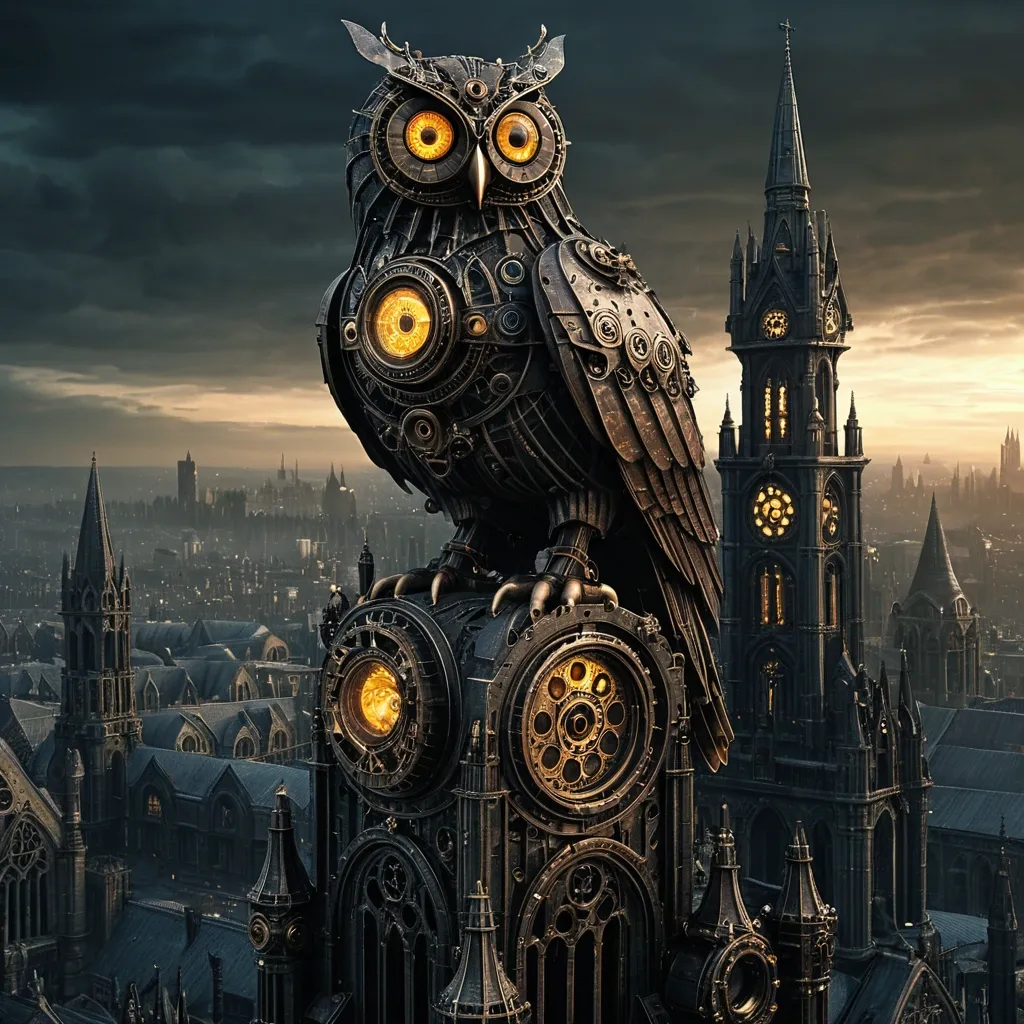

Highly creative. Wide shot. A colossal , sentient clockwork owl perched atop a crumbling gothic cathedral spire , surveying a city shrouded in perpetual twilight. Gears grind and steam hisses from its metallic body. Steampunk illustration. Intricate mechanical details , glowing amber eyes. Moody , volumetric lighting. Dark fantasy , industrial , mysterious , avant-garde , detailed. ar-9:16 ,
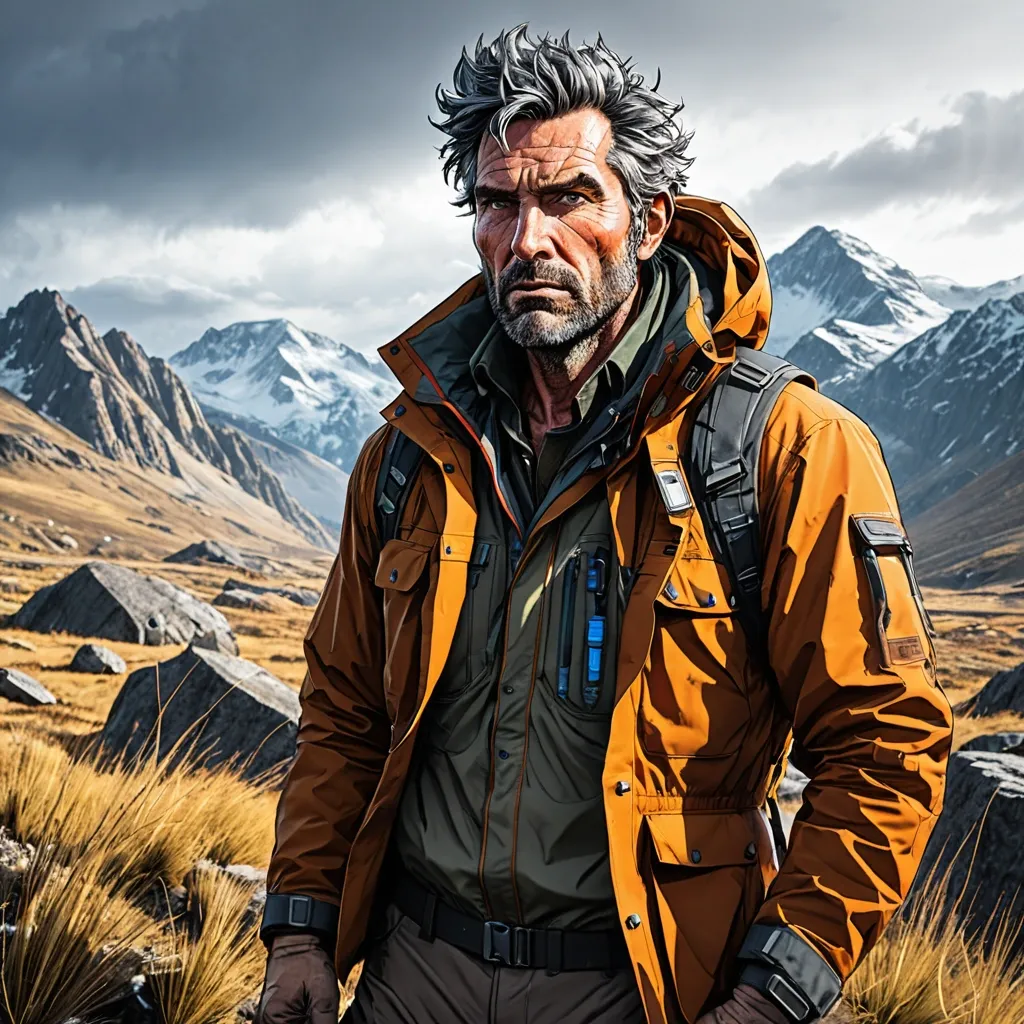

Young male geological surveyor , rugged , cautious , determined , experienced in wilderness , slightly messy hair , rough skin , sharp eyes , wearing simple explorer jacket , wilderness setting with rocks , dry grass , distant mountains , vast sky , manga style , high detail , clear lines , vivid colors , dynamic lighting , slight wind on clothes and hair , light mist atmosphere , low-angle composition , adventurous feeling. ,

Fairness means ensuring your analysis doesn't create or reinforce bias. This can be challenging , but if the analysis is not objective , the conclusions can be misleading and even harmful. In this reading , you’re going to explore some best practices you can use to guide your work toward a more fair analysis! Consider fairness Following are some strategies that support fair analysis: Best practice Explanation Example Consider all of the available data Part of your job as a data analyst is to determine what data is going to be useful for your analysis. Often there will be data that isn’t relevant to what you’re focusing on or doesn’t seem to align with your expectations. But you can’t just ignore it; it’s critical to consider all of the available data so that your analysis reflects the truth and not just your own expectations. A state’s Department of Transportation is interested in measuring traffic patterns on holidays. At first , they only include metrics related to traffic volumes and the fact that the days are holidays. But the data team realizes they failed to consider how weather on these holidays might also affect traffic volumes. Considering this additional data helps them gain more complete insights. Identify surrounding factors As you’ll learn throughout these courses , context is key for you and your stakeholders to understand the final conclusions of any analysis. Similar to considering all of the data , you also must understand surrounding factors that could influence the insights you’re gaining. A human resources department wants to better plan for employee vacation time in order to anticipate staffing needs. HR uses a list of national bank holidays as a key part of the data-gathering process. But they fail to consider important holidays that aren’t on the bank calendar , which introduces bias against employees who celebrate them. It also gives HR less useful results because bank holidays may not necessarily apply to their actual employee population. Include self-reported data Self-reporting is a data collection technique where participants provide information about themselves. Self-reported data can be a great way to introduce fairness in your data collection process. People bring conscious and unconscious bias to their observations about the world , including about other people. Using self-reporting methods to collect data can help avoid these observer biases. Additionally , separating self-reported data from other data you collect provides important context to your conclusions! A data analyst is working on a project for a brick-and-mortar retailer. Their goal is to learn more about their customer base. This data analyst knows they need to consider fairness when they collect data; they decide to create a survey so that customers can self-report information about themselves. By doing that , they avoid bias that might be introduced with other demographic data collection methods. For example , if they had sales associates report their observations about customers , they might introduce any unconscious bias the employees had to the data. Use oversampling effectively When collecting data about a population , it’s important to be aware of the actual makeup of that population. Sometimes , oversampling can help you represent groups in that population that otherwise wouldn’t be represented fairly. Oversampling is the process of increasing the sample size of nondominant groups in a population. This can help you better represent them and address imbalanced datasets. A fitness company is releasing new digital content for users of their equipment. They are interested in designing content that appeals to different users , knowing that different people may interact with their equipment in different ways. For example , part of their user-base is age 70 or older. In order to represent these users , they oversample them in their data. That way , decisions they make about their fitness content will be more inclusive. Think about fairness from beginning to end To ensure that your analysis and final conclusions are fair , be sure to consider fairness from the earliest stages of a project to when you act on the data insights. This means that data collection , cleaning , processing , and analysis are all performed with fairness in mind. A data team kicks off a project by including fairness measures in their data-collection process. These measures include oversampling their population and using self-reported data. However , they fail to inform stakeholders about these measures during the presentation. As a result , stakeholders leave with skewed understandings of the data. Learning from this experience , they add key information about fairness considerations to future stakeholder presentations. ,
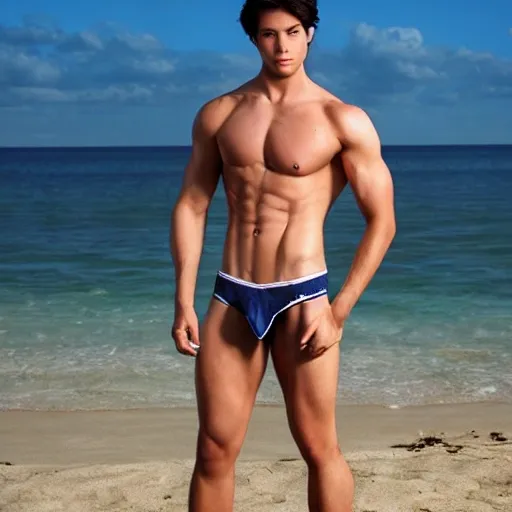

A realistic yet strikingly handsome anime man stands on the sandy shores of a beautiful beach , clad only in a pair of form-fitting navy blue boxer briefs. The sun beats down on his tanned , chiseled physique , with every muscle toned and defined to perfection. His short , spiky hair is ruffled by the ocean breeze , and his bright blue eyes survey the breathtaking scenery around him. His powerful arms and broad chest are on full display , as are the curves of his muscular legs. The waistband of his underwear sits low on his hips , revealing the subtle contours of his defined abs. His posture exudes a sense of strength and confidence , and his gaze is intense and focused. The details of his form , from the intricate folds of his underwear to the subtle lines and curves of his muscles , are rendered in stunningly lifelike detail , capturing the beauty and realism of anime art. ,
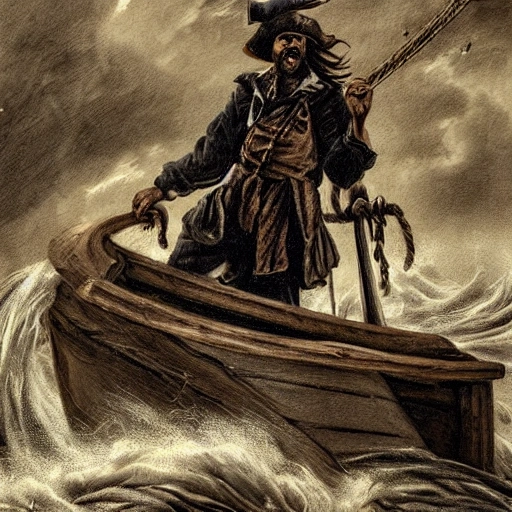

The pirate sailing through a storm is a striking and powerful figure , surrounded by the turbulence and chaos of the sea. He is dressed in rough and rugged clothing , suitable for the demands of life at sea , and he stands at the prow of his ship , surveying the stormy waters ahead. His physical appearance is weather-beaten and windswept , with long hair that is tossed about by the wind. He has a strong jawline , a broad chest , and a muscular build that exudes confidence and determination. Despite the raging storm , his expression is calm and focused , and his eyes are fixed on the horizon as he navigates his ship through the turbulent seas. The ship itself is battered and weathered , with torn sails and ropes whipping in the wind. The deck is slick with rain , and waves crash against the hull , sending sprays of saltwater into the air. The sky overhead is dark and foreboding , with lightning flashing across the clouds and thunder echoing through the air. Despite the storm , the pirate is at ease , confident in his abilities and in the strength of his ship. He stands tall and proud , a symbol of the fearless spirit of the sea and the adventurers who dare to brave its storms. , Cartoon ,
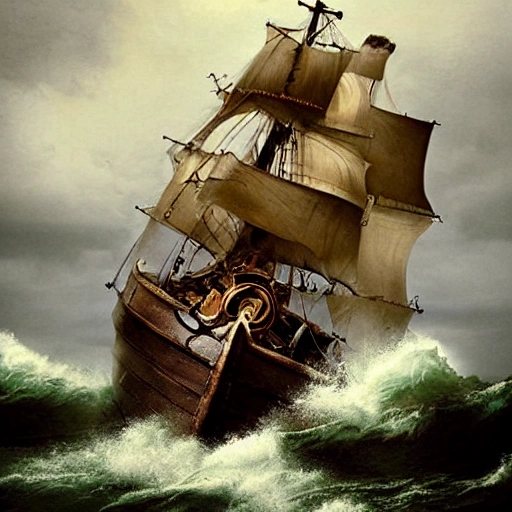

The pirate sailing through a storm is a striking and powerful figure , surrounded by the turbulence and chaos of the sea. He is dressed in rough and rugged clothing , suitable for the demands of life at sea , and he stands at the prow of his ship , surveying the stormy waters ahead. His physical appearance is weather-beaten and windswept , with long hair that is tossed about by the wind. He has a strong jawline , a broad chest , and a muscular build that exudes confidence and determination. Despite the raging storm , his expression is calm and focused , and his eyes are fixed on the horizon as he navigates his ship through the turbulent seas. The ship itself is battered and weathered , with torn sails and ropes whipping in the wind. The deck is slick with rain , and waves crash against the hull , sending sprays of saltwater into the air. The sky overhead is dark and foreboding , with lightning flashing across the clouds and thunder echoing through the air. Despite the storm , the pirate is at ease , confident in his abilities and in the strength of his ship. He stands tall and proud , a symbol of the fearless spirit of the sea and the adventurers who dare to brave its storms. , Cartoon , Oil Painting ,